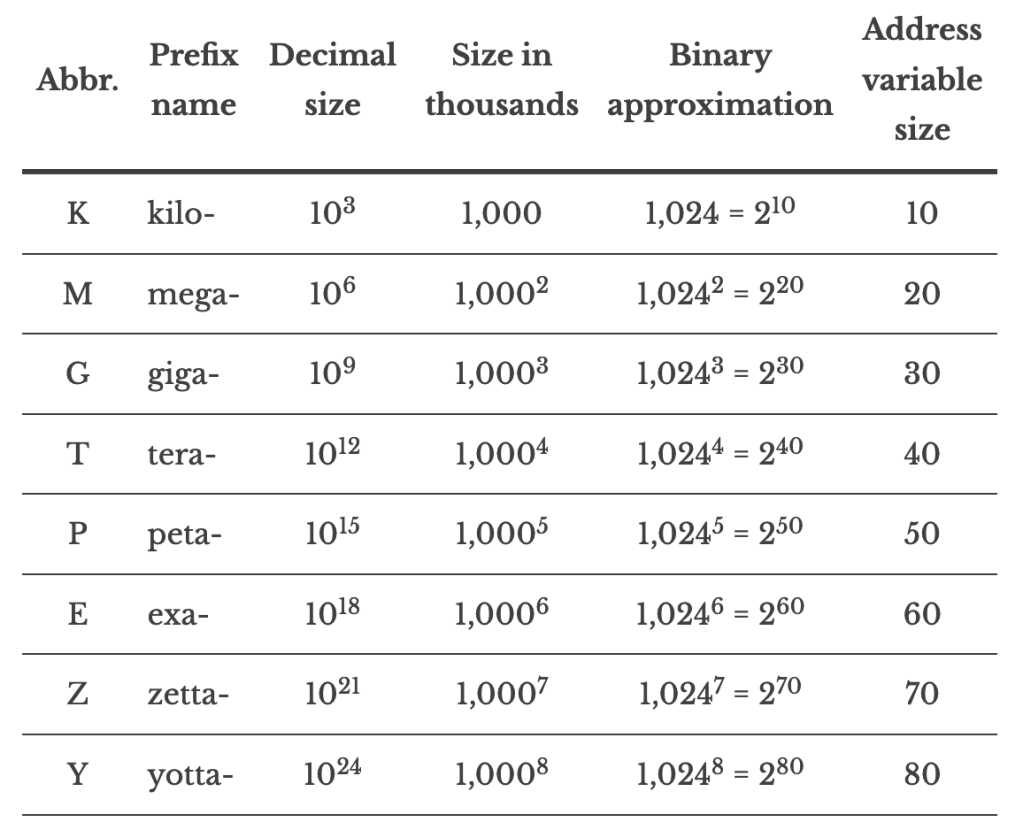
One of the most popular pages on this site provides a simple conversion to map numbers of various sizes to the corresponding memory storage sizes in bits (mathematicians and other geeks often call this “log base 2”). The popular table now includes all of the international standard integer size names. I’ve also expanded the discussion of inaccuracies between decimal and binary (“power of 2,” really) naming.
Address Size Shortcut
Here is a simple shortcut for estimating the number of bits required to address storage of a given size. This is good for “first guess” estimates ONLY. There have been lawsuits over using a base-10 size versus a base-2 size to describe a storage size.
103 ~ 210
To put this into practice, we do the following:
- Count the number of sets of three zeros (the “thousands”) in the storage size.
- Multiply the number of thousands by ten
Let’s work out an example with a terabyte: a trillion-byte memory.
- In a trillion (1,000,000,000,000) there are 4 sets of three zeroes
- Multiply 4 by 10, and we get approximately 40 bits.

You must be logged in to post a comment.